This page will look to give a clear introduction to area measure in Math.
2D Area, Square and Rectangle
When dealing with 2 dimensions (2D), area is the measure of the amount of space there is on a flat surface, enclosed within a certain boundary.Likely the simplest shape to look at for an introduction to area measure in 2D is a square or a rectangle shape.
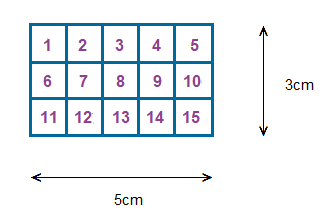
The rectangle dispalyed above, is 3cm high, and also 5cm wide.
It is comprised of 15 smaller squares, of which each is 1cm high, and 1cm wide.
Rather than counting all of the smaller squares individually though, when we have to establish the area of a standard square or rectangle.
We can perform the sum of multiplying the width by the height.
So for the rectangle we see above.
5 × 3 = 15
The total area of the whole rectangle is 15 square centimetres.
Introduction to Area Measure, Dimensions
It’s important to make sure that the dimensions are the same on all sides of a shape in 2D area.
For example a rectangle could be presented as:
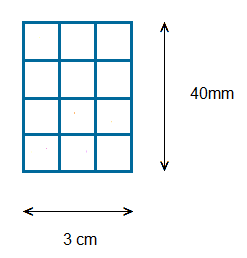
For the total area in square centimetres, we would be required to convert the height shown from millimetres to centimetres.
40 millimetres is 4 centimetres.
Area = 4 × 3 = 12 , 12 square centimetres
Area Notation
The right notation for area values is important to learn and remember.Rather than writing out the words square centimetres, a shorter notation of cm2 is generally used.
Likewise if the measure of an area in metres, m2 is the notation used.
The relevant unit being measured, with an index of 2.
Example

(1.1)
What is the area in square metres of a rectangular garden that is 8 metres wide, and 700 centimetres long.
Solution
700 centimetres is 7 metres. 700cm = 7m
8 × 7 = 56 , The total area of the rectangular garden is 56m2.
Units of Area
Like in the case of length, it’s important to note in an introduction to area measure that area can be measured using a range of different units.In cases above we’ve seen centimetres and metres, but there are other values of area measure that can be seen in Geometry.
The size of rooms and floors in building plans for example are often measured in square feet, ft2.
Very large land areas such as countries are generally measured and displayed in square miles, mi2, or square kilometres, km2.
In each situation though, it’s the same idea as the first example on this page.
What amount of smaller squares are there that cover a larger surface area.