This page aims to give an introduction to what Algebra functions are, and how they are represented with functions notation in Algebra.
What is a Function?
A function in Algebra is a definition of a relationship between numbers.A rule that assigns, for each number/element of a certain set, say a of set A.
To a unique element of a different set, say b of set B.
The situation can be illustrated to show the process.
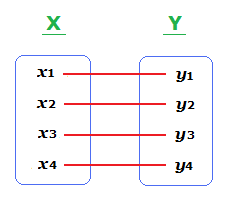
Functions Notation in Algebra
The common notation for functions in Algebra is: f(x) = y.
Where f(x) represents a function involving a value x.
The letter f denotes the function, with an x value going into the function, and a y value coming out.
The letters for the values in function notation don’t have to always be x and y.
For example, f(a) = b denotes a function, the value a goes in, and a value b comes out.
Also, f doesn’t always have to be the letter that represents the function.
We can write h(x) = y, which can denote a function, from x to y.
Sometimes you can see a function also be denoted f : x → y.
A function from a set X to a set Y.
Functions Domain and Range
Consider the function f(x) = 3x + 2.
On a set X comprising of the values [ 1 , 2 , 5 , 7 ].
f(1) = 3(1) + 2 = 3 + 2 = 5
f(2) = 3(2) + 2 = 6 + 2 = 8
f(5) = 3(5) + 2 = 15 + 2 = 17
f(7) = 3(7) + 2 = 21 + 2 = 23
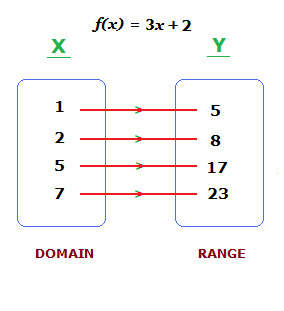
Set X is the ‘domain’, which is the set of the values that are being put into the function.
Set Y is the ‘range’ or image, this set contains the values that are coming out of the function.
At times set Y can include some extra values, that aren’t connected to any of the values in set X by the relevant function.
When this happens to be the case, set Y is classed as the as the co-domain, which we can see illustrated below.
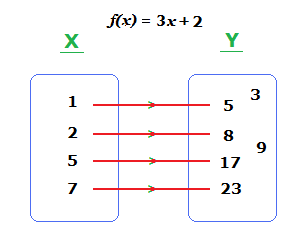
Along with being written as f(x) = 3x + 2.
Such a standard function can also be written as y = 3x + 2.
Seeing as it’s the y value coming out, when an x value has gone in.